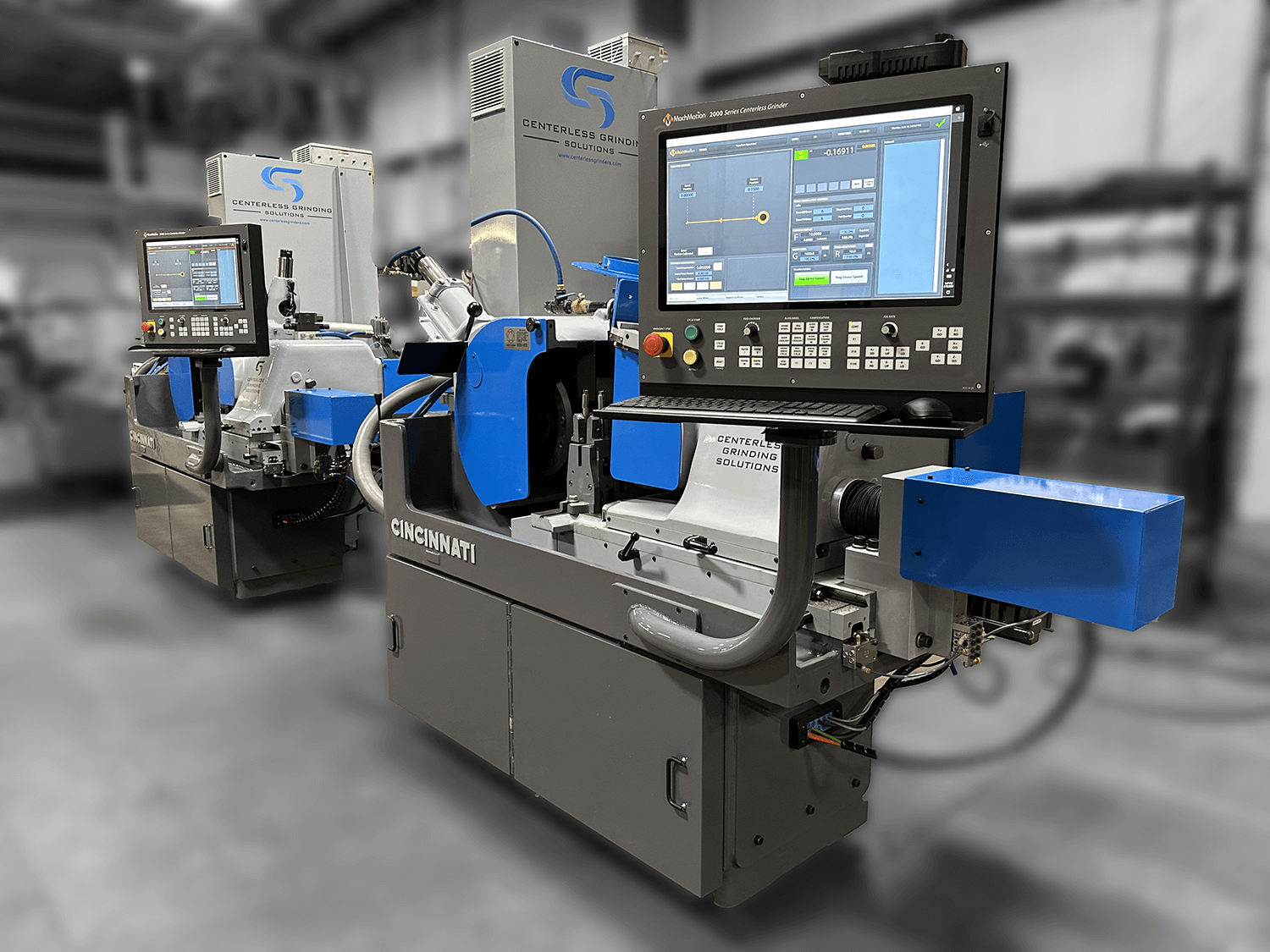
The Complete Guide to the Centerless Grinding Process
For maintenance managers, plant operators, and manufacturing decision-makers, understanding the centerless grinding process is essential. This method delivers precision that other approaches can’t match, maintains tight tolerances, and provides production efficiency that directly impacts your bottom line.
This comprehensive guide covers everything you need to know about the centerless grinding process: how it works, its advantages, best practices for optimal performance, and strategies for long-term success.
What Is the Centerless Grinding Process?
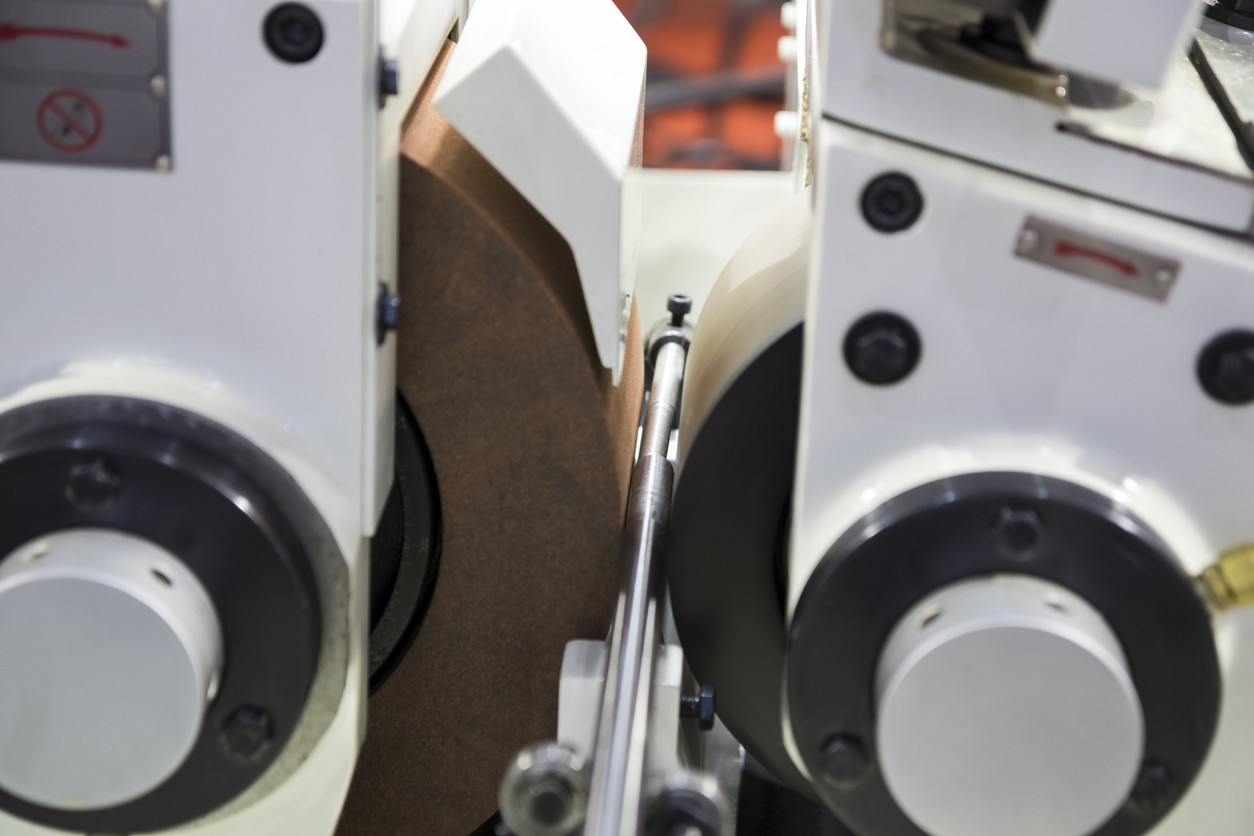
Centerless grinding removes material from a workpiece without holding it in a spindle or fixture. Instead, the part rests on a work rest blade positioned between two wheels: a grinding wheel that removes material and a regulating wheel that controls rotation and feed rate.
This fundamental difference creates significant advantages over conventional grinding methods.
The process produces a 1:1 ratio of material removal to grinding wheel movement. For every 0.001 inch the wheel moves in, exactly 0.001 inch comes off the workpiece diameter. That makes centerless grinding twice as accurate as traditional OD or ID grinding.
Parts align themselves naturally during the process. They reference only the diameter being ground, eliminating cumulative errors from multiple setups and fixtures that plague other grinding methods.
The result is a process capable of holding tolerances within 0.0001 inch while maintaining exceptional surface finishes and high production rates.
Key Components of the Centerless Grinding Process
Understanding each component’s role helps you optimize performance and troubleshoot issues when they arise.
The Grinding Wheel
The grinding wheel performs the actual material removal. It rotates at high speed—typically 4,000 to 6,500 surface feet per minute—and its abrasive grains cut away material to achieve the target dimension and surface finish.
Wheel specification matters significantly. Grain type, grit size, grade, and bond system must match your workpiece material, removal rate requirements, and desired surface finish.
The Regulating Wheel
The regulating wheel controls workpiece rotation speed and, in throughfeed operations, the feed rate through the grinding zone. It typically runs at much slower speeds than the grinding wheel—usually 50 to 200 surface feet per minute.
This wheel’s surface is usually rubber-bonded abrasive or solid rubber, providing the friction needed to drive the workpiece without damaging it.
The Workrest Blade
The workrest blade supports the workpiece during grinding. Its position, angle, and condition directly affect part geometry, surface finish, and dimensional accuracy.
Blade geometry creates the reference surface that determines how the part contacts both wheels, making it crucial for achieving consistent results.
Mastering Wheel Dressing in the Centerless Grinding Process
Grinding wheel condition directly impacts part quality and production efficiency. Dull wheels generate excessive heat, create poor surface finishes, and require more passes to achieve target dimensions.
Your dressing intervals should respond to what you’re grinding, not a fixed schedule.
Harder materials dull wheels faster. Higher removal rates accelerate wear. Tighter tolerances demand more frequent dressing to maintain consistent results.
Monitor your parts continuously. When you notice surface finish degradation or dimensional drift, you’ve waited too long. Dress the wheel before quality suffers, not after.
Modern operations track dressing frequency against part counts and material types. This data reveals patterns that optimize both wheel life and part quality.
Optimizing Work Rest Blade Geometry
The work rest blade supports your workpiece during grinding. Its angle, height, and condition determine whether you achieve target tolerances or generate scrap.
Blade height positions the workpiece relative to the grinding and regulating wheel centerlines. Too high or too low creates geometry problems that no amount of wheel adjustment can fix.
The blade angle affects how the part enters and exits the grinding zone. Incorrect angles cause chatter, poor finishes, and dimensional inconsistencies.
Replace blades showing wear or damage immediately. A worn blade edge creates an unstable support surface that introduces vibration and dimensional variation.
Document your blade settings for different part families. When you find configurations that consistently deliver quality results, standardize them across shifts and operators.
Controlling Regulating Wheel Variables
The regulating wheel does more than rotate your workpiece. It controls feed rate, affects surface finish, and influences dimensional accuracy.
Wheel speed determines how fast material moves through the grinding zone. Too fast creates excessive heat and poor finishes. Too slow reduces productivity and can cause loading.
Wheel condition matters as much as the grinding wheel. A glazed or loaded regulating wheel slips instead of driving the workpiece consistently. This creates dimensional variation and surface finish problems.
Dress your regulating wheel on a schedule appropriate to your production volume and materials. High-volume operations may need daily dressing. Lower volumes might extend intervals, but never skip condition checks.
The regulating wheel diameter changes as it wears. Compensate for this wear in your setup calculations, or you’ll see gradual dimensional drift across production runs.
Implementing Predictive Maintenance for Process Reliability
Reactive maintenance costs you production time and emergency repair expenses. Predictive maintenance catches problems before they stop your line.
Predictive approaches reduce replacement parts needs by up to 40%. They also eliminate most unplanned downtime by addressing wear before failure occurs.
Monitor spindle bearing temperatures during operation. Rising temperatures indicate developing problems with lubrication or bearing condition. Catch these early, and you schedule repairs during planned downtime instead of emergency stops.
Check wheel balance regularly. Imbalanced wheels create vibration that damages bearings, reduces part quality, and accelerates component wear throughout the machine.
Inspect hydraulic systems for leaks, pressure consistency, and fluid condition. Hydraulic problems rarely announce themselves until they cause complete failures.
Document everything. Maintenance logs reveal patterns that predict future problems and optimize service intervals.
Standardizing Setup Procedures for Consistent Results
Setup variation creates quality variation. When different operators use different approaches, you get different results even on identical parts.
Develop written setup procedures for your common part families. Include wheel speeds, feed rates, blade positions, and dressing intervals. Make these procedures accessible at the machine.
Use setup sheets that operators complete and sign. This creates accountability and provides data for troubleshooting when quality issues emerge.
Photograph correct setups. Visual references reduce setup time and eliminate guesswork, especially for operators who run a part infrequently.
Train all operators on your standardized procedures. Consistency across shifts prevents quality surprises and reduces scrap rates.
Extending Equipment Life Through Remanufacturing
Even well-maintained centerless grinders eventually need major service. Components wear, technology advances, and performance degrades.
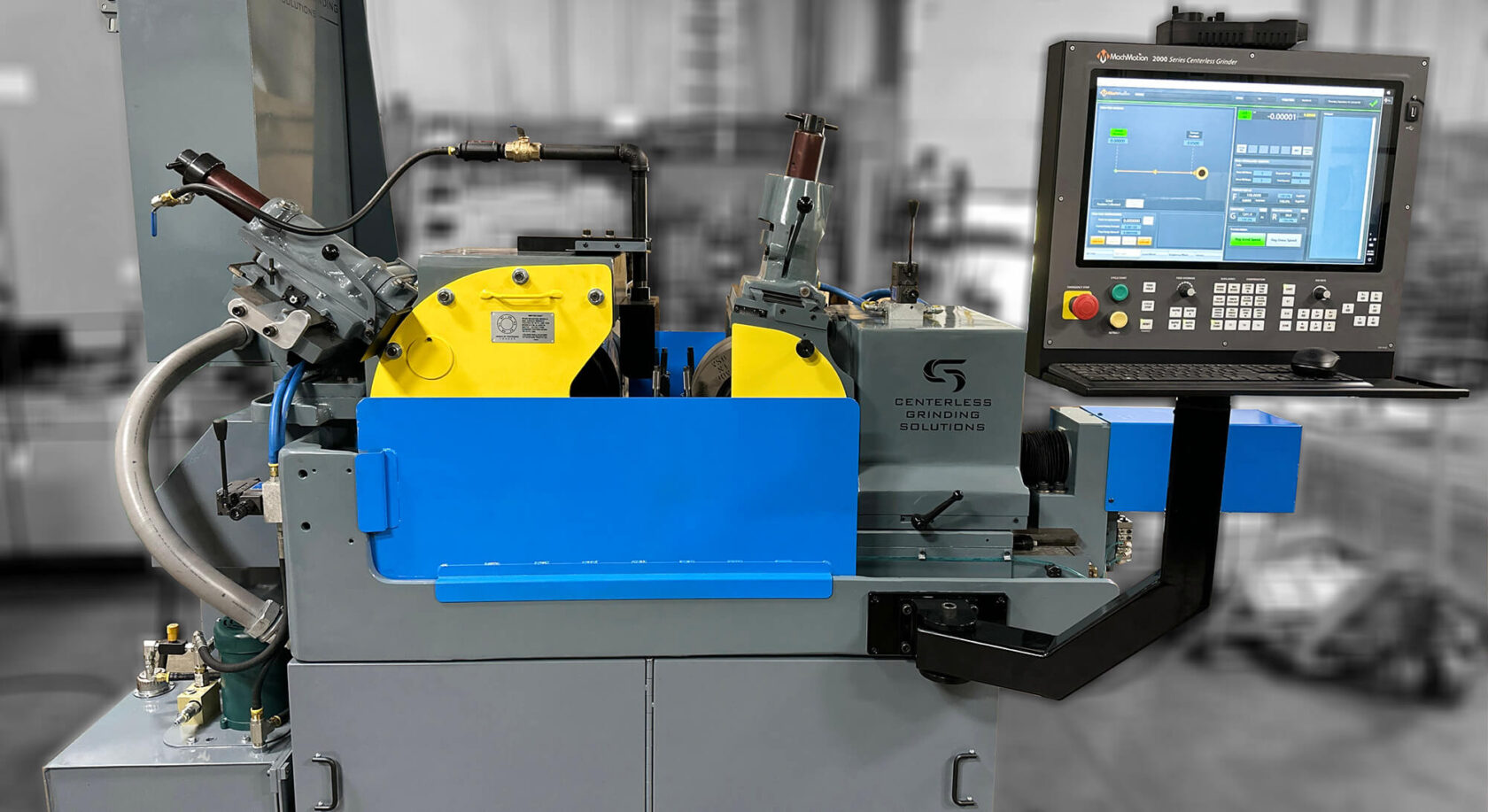
Remanufacturing extends equipment life while integrating modern improvements. A properly remanufactured machine operates like new equipment, often with better capabilities than the original configuration.
The economics favor remanufacturing. You save 30 to 50 percent compared to new equipment costs while maintaining the machine knowledge your operators already possess.
Modern remanufacturing incorporates current technology into proven platforms. CNC controls replace manual systems. Updated automation reduces setup time and improves repeatability. Enhanced safety features protect operators.
The key is working with specialists who understand centerless grinding specifically. General machine shops lack the expertise to properly rebuild grinding machines to original tolerances and performance standards.
At Centerless Grinding Solutions, we’ve remanufactured centerless grinders for over 30 years. We don’t just rebuild machines. We modernize them with current technology while preserving the reliability that made them valuable in the first place.
Maintaining Parts Inventory for Process Continuity
Nothing stops production faster than waiting for a replacement part. When a critical component fails, every hour of downtime multiplies across your entire operation.
Identify the parts most likely to need replacement. Grinding wheels, regulating wheels, workrest blades, and spindle components top most lists.
Maintain inventory appropriate to your production volume and part criticality. High-volume operations justify larger inventories. Lower volumes can work with suppliers who stock common components and ship quickly.
Consider your machine’s age and parts availability. Older machines, especially discontinued models, require more extensive spare parts inventory because replacement components become harder to source over time.
We maintain a comprehensive inventory of centerless grinder parts and components. Our stock includes parts for Cincinnati, Landis, and other major manufacturers, including discontinued models that other suppliers can’t support.
Developing Operator Expertise for Process Excellence
Your equipment’s performance depends on operator knowledge and skill. The best machine with poor operators delivers mediocre results.
Train operators on the fundamentals of centerless grinding. When they understand how blade position, wheel speeds, and feed rates interact, they make better decisions during setup and production.
Teach troubleshooting skills. Operators who can identify and correct minor issues prevent them from becoming major problems that require maintenance intervention.
Cross-train operators across multiple machines. This flexibility helps you maintain production when someone is absent and spreads institutional knowledge across your team.
We work with manufacturers to develop operator knowledge. Our team shares expertise gained from three decades in centerless grinding, helping your operators understand both the equipment and the process.
Optimizing Your Centerless Grinding Process
Understanding the centerless grinding process provides the foundation. Optimizing it delivers results that impact your production efficiency, part quality, and operational costs.
The principles covered in this guide—proper wheel maintenance, precise blade geometry, controlled regulating wheel variables, predictive maintenance, standardized procedures, strategic remanufacturing, adequate parts inventory, and skilled operators—work together to create a reliable, high-performance grinding operation.
Implementation requires commitment. Document your procedures. Train your team thoroughly. Monitor performance consistently. Measure results systematically.
When you identify gaps between your current operations and the principles outlined here, prioritize based on impact. Start with changes that deliver immediate improvements in uptime, quality, or cost reduction.
Your centerless grinding process can achieve exceptional precision, outstanding reliability, and optimal cost efficiency. The path forward combines technical understanding with proven operational practices and equipment that’s properly maintained, appropriately upgraded, and supported by genuine expertise.
At Centerless Grinding Solutions, we’ve spent over 30 years helping manufacturers master the centerless grinding process. From machine remanufacturing to parts supply to technical support, we provide the resources you need to optimize your operations successfully.
Your operations deserve equipment that performs reliably and expertise you can trust when challenges emerge.